Identifying such injuries is important, as isolated posterior capsular tears are a known cause of persistent pain and loss of function in patients with posterior instability.16. The findings are compatible with a posterior GLAD lesion (glenolabral articular disruption). Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. Unable to process the form. Imaging in three planes is advisable and additional orthogonal planes may be included in the protocol for a detailed assessment of the lesion. Notice the detatched labrum at the 6-9 o'clock position on the sagittal MR-arthrogram. Notice extention of the SLAP-tear further to posterior (red arrow). Posterior Glenohumeral Instability Superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP)tears are injuries of the glenoid labrum,and can often be confused with a sublabral sulcus on MRI. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle Popp D & Schffl V. Superior Labral Anterior Posterior Lesions of the Shoulder: Current Diagnostic and Therapeutic Standards. Because the arthroscope and surgical instruments are thin, your surgeon can use very small incisions (cuts), rather than the larger incision needed for standard, open surgery. Snyder et al. A posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) is also present (arrowhead), and a bone bruise is seen within the anterior humeral head (asterisk). Posterior instability lesions include the reverse Bankart (Figure 5a), the posterior labrum periosteal sleeve avulsion injury (POLPSA) (Figure 6a), and the posterior band inferior glenohumeral ligament avulsion from the humerus (PHAGL) (Figure 7a).7,8, The MRI findings in these patients often provide useful indicators of clinical significance. It also serves as an attachment point for many of the ligaments of the shoulder, as well as one of the tendons from the biceps muscle in the arm. This test can better show soft tissues like the labrum. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. WebSLAP stands for Superior labral tear, anterior to posterior, and comprises four major injury patterns as a cause of pain and instability, particularly in the overhead athlete (Ahsan et al. Glenoid labral tears are the injuries of the glenoid labrum and a possible cause of shoulder pain. The dislocation of the humeral head to antero-inferior causes damage to the antero-inferior rim of the glenoid in the 3 - 6 o'clock position (marked in red). Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. Tears to the specialized cartilage tissue in the shoulder known as the labrum can cause pain and instability in the shoulder. MR interpreters should be aware that at Keith W. Harper1, Clyde A. Helms1, Clare M. Haystead1 and Lawrence D. Higgins Glenoid Dysplasia: Incidence and Association with Posterior Labral Tears as Evaluated on MRI. An acute SLAP injury may result from: People who participate in repetitive overhead sports, such as throwing athletes or weightlifters, can experience labrum tears as a result of repeated shoulder motion. An impaction fracture is also present at the posterior glenoid rim (blue arrow).  A mid-substance tear of the posterior capsule is present with the medial component appearing lax and retracted (arrow). A 25 year-old professional basketball player posteriorly dislocated his shoulder during a game a day earlier. Posterior shoulder subluxation or dislocation is also one of the rare entities that may result in tears of the teres minor muscle.18 MR allows rapid evaluation of the status of the cuff following posterior dislocation, and prompt diagnosis of such lesions avoids delays in treatments that may lead to irreversible fatty atrophy of cuff musculature (Figs. Clinical History: A 72 year-old male presents with severe left shoulder pain and limited motion following a fall 10 days earlier. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. 4 Harper KW, Helms CA, Haystead CM, Higgins LD. 6,11,16,17 In the current study, 244 of the shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrated a posterior glenoid labral tear WebThe labrum can tear a few different ways: 1) completely off the bone, 2) within or along the edge of the labrum, or 3) where the bicep tendon attaches. Mild glenoid hypoplasia results in a rounded contour of the posterior glenoid with normal or only mildly thickened posterior labral tissue. A posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) is also present (arrowhead), and a bone bruise is seen within the anterior humeral head (asterisk). 14). Lesions of the labrum, rotator cuff musculature, and glenoid may contribute to recurrent posterior glenohumeral subluxation. (4a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a severely retroverted glenoid (arrowheads) and posterior glenoid hypoplasia with a hypertrophied posterior labrum (arrow). Such injuries may be referred to as reverse HAGL (humeral avulsion of the glenohumeral ligament) or RHAGL lesions (Fig. Shah N and Tung GA. 174 no. Sometimes an axillary view can be of help, but when in doubt go to CT. Such lesions are generally found in patients with atraumatic posterior instability. There is an ongoing debate on whether direct MR arthrography is superior to conventional MR in detecting labral tears. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. This in turn creates instability because the breached labrum makes it easier for the shoulder to dislocate again. Webshoulder. Smith T, Drew B, Toms A. Approximately half of the posterior shoulder dislocations go undiagnosed on initial presentation, because of a low level of clinical suspicion and insufficient imaging. 6. CT and MR Arthrography of the Normal and Pathologic Anterosuperior Labrum and Labral-Bicipital Complex. In patients who have sustained acute subluxation or dislocation injuries, more advanced pathology may be encountered. However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. 2003;181(6):1449-62. 9 Tung GA, Hou DD. First notice the Hill-Sachs defect indicating a prior anterior dislocation (blue arrow). J Bone Joint Surg Am. This is especially the case in older adults, because our cartilage becomes more brittle with age. 2005;184: 984-988. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. Snyder et al. The arrow points to the cartilage defect. Plain film and CT may be utilized to evaluate bony contour abnormalities such as the reverse Bankart lesion or retroversion of the glenoid. In the ABER-position it is obvious that there is a Perthes lesion (black arrow). The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. The only exception to this rule is the reverse Bankart, which is the result of a posterior dislocation and injury to the inferoposterior labrum. As a result, in cases of posterior shoulder instability, particularly dislocation, capsular tears are frequently identified on MR imaging.14 The posterior capsule injuries most commonly involve the humeral attachment inferiorly15, in the region known as the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament. The example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well. Musculoskeletal Imaging,The Requisites (Expert Consult- Online and Print),4. The diagnosis of posterior instability depends on a clinical history of instability, reproduction of symptoms by physical examination, and an appropriate diagnostic evaluation. endobj
HAGL is a Humeral Avulsion of the inferior Glenohumeral Ligament. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an Acute traumatic posterior shoulder dislocation: MR findings. The structure anterior to the glenoid is not a thorn labrum, but the middle glenohumeral ligament. Sports Health 2011 May, 3(3):253-263, Cooper A. Figure 1. (3a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a rounded posterior margin (arrows) and a prominently hypertrophied posterior labrum (arrowhead) compatible with posterior glenoid hypoplasia. 2000 Jun; 82(6):849-57. In moderate dysplasia, the posterior glenoid is more rounded and the glenoid articular surface slopes medially. Potential problems with arthroscopy include infection, excessive bleeding, blood clots, shoulder stiffness, and damage to blood vessels or nerves. In: Post M, Morrey BF, Hawkins RJ, editors. MRA( ) . They can extend into the tendon, involve the glenohumeral ligaments or extend into other quadrants of the labrum. Modern imaging techniques, in particular MRI, have greatly increased our ability to accurately diagnose posterior glenohumeral instability, and accurate recognition and characterization of the relevant abnormalities are critical for proper diagnosis and patient management.5, Multiple shoulder structures are important in resisting shoulder instability. %
no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Treatment options may include: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication. Chung CB, Sorenson S, Dwek JR and Resnick D. Humeral Avulsion of the Posterior Band of the Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament: MR Arthrography and Clinical Correlation in 17 Patients. Your doctor may recommend surgery if your pain does not improve with nonsurgical methods. Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Nyffeler RW, Gerber C, Hodler J. Posterior glenoid rim deficiency in recurrent (atraumatic) posterior shoulder instability. Glenoid dysplasia, also referred to as glenoid hypoplasia and posterior glenoid rim deficiency, is now increasingly recognized as an anatomic variant that predisposes patients to posterior glenohumeral instability. However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. In patients over 40 years of age, tearing or fraying of the superior labrum can be seen as a normal process of aging. The red arrow points to the absent labrum - Buford complex. Mr Watson will discuss with you when it is safe to return to sports activity. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an Normal shoulder MRI. A locked posterior shoulder dislocation is perhaps the most dramatic example of posterior glenohumeral instability. (2001) ISBN: 0721690270 -. Surgeons will usually conduct a physical exam and order MRI or X-ray imaging, if necessary, to determine the severity of the injury and the appropriate treatment. The epidemiology and biomechanics of throwing injuries are reviewed, and examples from the authors institutional experience with competitive, collegiate, and professional baseball players are provided to demonstrate the constellation of unique imaging findings seen in overhead throwing athletes. dekalb county circuit clerk forms; zander capital management fargo, nd; patricia mcpherson interview A SLAP tear occurs both in front (anterior) and back (posterior) of this attachment point. Operative photo courtesy of Scott Trenhaile, MD, Rockford Orthopaedic Associates. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 79A:433-40, 1997. On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. Repair options. 2000;20 Spec No(suppl_1):S67-81. Check for errors and try again. Images of a MR-arthrogram. Here another patient with an osseus Bankart seen on four consecutive images of a MR arthrogram in ABER-view. Snyder et al.
A mid-substance tear of the posterior capsule is present with the medial component appearing lax and retracted (arrow). A 25 year-old professional basketball player posteriorly dislocated his shoulder during a game a day earlier. Posterior shoulder subluxation or dislocation is also one of the rare entities that may result in tears of the teres minor muscle.18 MR allows rapid evaluation of the status of the cuff following posterior dislocation, and prompt diagnosis of such lesions avoids delays in treatments that may lead to irreversible fatty atrophy of cuff musculature (Figs. Clinical History: A 72 year-old male presents with severe left shoulder pain and limited motion following a fall 10 days earlier. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. 4 Harper KW, Helms CA, Haystead CM, Higgins LD. 6,11,16,17 In the current study, 244 of the shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrated a posterior glenoid labral tear WebThe labrum can tear a few different ways: 1) completely off the bone, 2) within or along the edge of the labrum, or 3) where the bicep tendon attaches. Mild glenoid hypoplasia results in a rounded contour of the posterior glenoid with normal or only mildly thickened posterior labral tissue. A posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) is also present (arrowhead), and a bone bruise is seen within the anterior humeral head (asterisk). 14). Lesions of the labrum, rotator cuff musculature, and glenoid may contribute to recurrent posterior glenohumeral subluxation. (4a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a severely retroverted glenoid (arrowheads) and posterior glenoid hypoplasia with a hypertrophied posterior labrum (arrow). Such injuries may be referred to as reverse HAGL (humeral avulsion of the glenohumeral ligament) or RHAGL lesions (Fig. Shah N and Tung GA. 174 no. Sometimes an axillary view can be of help, but when in doubt go to CT. Such lesions are generally found in patients with atraumatic posterior instability. There is an ongoing debate on whether direct MR arthrography is superior to conventional MR in detecting labral tears. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. This in turn creates instability because the breached labrum makes it easier for the shoulder to dislocate again. Webshoulder. Smith T, Drew B, Toms A. Approximately half of the posterior shoulder dislocations go undiagnosed on initial presentation, because of a low level of clinical suspicion and insufficient imaging. 6. CT and MR Arthrography of the Normal and Pathologic Anterosuperior Labrum and Labral-Bicipital Complex. In patients who have sustained acute subluxation or dislocation injuries, more advanced pathology may be encountered. However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. 2003;181(6):1449-62. 9 Tung GA, Hou DD. First notice the Hill-Sachs defect indicating a prior anterior dislocation (blue arrow). J Bone Joint Surg Am. This is especially the case in older adults, because our cartilage becomes more brittle with age. 2005;184: 984-988. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. Snyder et al. The arrow points to the cartilage defect. Plain film and CT may be utilized to evaluate bony contour abnormalities such as the reverse Bankart lesion or retroversion of the glenoid. In the ABER-position it is obvious that there is a Perthes lesion (black arrow). The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. The only exception to this rule is the reverse Bankart, which is the result of a posterior dislocation and injury to the inferoposterior labrum. As a result, in cases of posterior shoulder instability, particularly dislocation, capsular tears are frequently identified on MR imaging.14 The posterior capsule injuries most commonly involve the humeral attachment inferiorly15, in the region known as the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament. The example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well. Musculoskeletal Imaging,The Requisites (Expert Consult- Online and Print),4. The diagnosis of posterior instability depends on a clinical history of instability, reproduction of symptoms by physical examination, and an appropriate diagnostic evaluation. endobj
HAGL is a Humeral Avulsion of the inferior Glenohumeral Ligament. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an Acute traumatic posterior shoulder dislocation: MR findings. The structure anterior to the glenoid is not a thorn labrum, but the middle glenohumeral ligament. Sports Health 2011 May, 3(3):253-263, Cooper A. Figure 1. (3a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a rounded posterior margin (arrows) and a prominently hypertrophied posterior labrum (arrowhead) compatible with posterior glenoid hypoplasia. 2000 Jun; 82(6):849-57. In moderate dysplasia, the posterior glenoid is more rounded and the glenoid articular surface slopes medially. Potential problems with arthroscopy include infection, excessive bleeding, blood clots, shoulder stiffness, and damage to blood vessels or nerves. In: Post M, Morrey BF, Hawkins RJ, editors. MRA( ) . They can extend into the tendon, involve the glenohumeral ligaments or extend into other quadrants of the labrum. Modern imaging techniques, in particular MRI, have greatly increased our ability to accurately diagnose posterior glenohumeral instability, and accurate recognition and characterization of the relevant abnormalities are critical for proper diagnosis and patient management.5, Multiple shoulder structures are important in resisting shoulder instability. %
no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Treatment options may include: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication. Chung CB, Sorenson S, Dwek JR and Resnick D. Humeral Avulsion of the Posterior Band of the Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament: MR Arthrography and Clinical Correlation in 17 Patients. Your doctor may recommend surgery if your pain does not improve with nonsurgical methods. Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Nyffeler RW, Gerber C, Hodler J. Posterior glenoid rim deficiency in recurrent (atraumatic) posterior shoulder instability. Glenoid dysplasia, also referred to as glenoid hypoplasia and posterior glenoid rim deficiency, is now increasingly recognized as an anatomic variant that predisposes patients to posterior glenohumeral instability. However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. In patients over 40 years of age, tearing or fraying of the superior labrum can be seen as a normal process of aging. The red arrow points to the absent labrum - Buford complex. Mr Watson will discuss with you when it is safe to return to sports activity. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an Normal shoulder MRI. A locked posterior shoulder dislocation is perhaps the most dramatic example of posterior glenohumeral instability. (2001) ISBN: 0721690270 -. Surgeons will usually conduct a physical exam and order MRI or X-ray imaging, if necessary, to determine the severity of the injury and the appropriate treatment. The epidemiology and biomechanics of throwing injuries are reviewed, and examples from the authors institutional experience with competitive, collegiate, and professional baseball players are provided to demonstrate the constellation of unique imaging findings seen in overhead throwing athletes. dekalb county circuit clerk forms; zander capital management fargo, nd; patricia mcpherson interview A SLAP tear occurs both in front (anterior) and back (posterior) of this attachment point. Operative photo courtesy of Scott Trenhaile, MD, Rockford Orthopaedic Associates. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 79A:433-40, 1997. On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. Repair options. 2000;20 Spec No(suppl_1):S67-81. Check for errors and try again. Images of a MR-arthrogram. Here another patient with an osseus Bankart seen on four consecutive images of a MR arthrogram in ABER-view. Snyder et al. 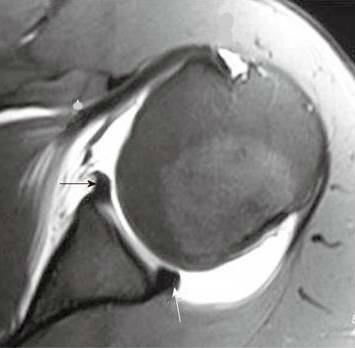 This type of tear occurs at the front of the upper arm where the biceps tendon connects to the shoulder. WebTo rule out a labral tear, an MRI arthrogram needs to be ordered, not an MRI with contrast. Recurrent posterior subluxation is the most common form of posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency. At the time the article was created Magdalena Chmiel-Nowak had no recorded disclosures. On coronal images you want to make sure whether this is a variant like a labral recess or labral foramen or whether this is a SLAP. 11 ). This was an incidental finding on a chest-film. Your doctor may also examine your neck and head to make sure that your pain is not coming from a pinched nerve.. Reading time: 18 minutes. Variations in osseous anatomy at the glenoid can significantly affect shoulder stability. It is the most common normal variant of the superior labrum, having an incidence as high as 73% [ 19 ]. Skeletal Radiol. (2013) ISBN: 9780323081771 -. This cyst can also cause posterior shoulder pain, and when it is large, it can compress the suprascapular nerve, causing weakness of shoulder rotation. On conventional MR labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences. Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. 4). McCauley T. MR Imaging of the Glenoid Labrum. 6 1707-1715. by Michel De Maeseneer et al When the shoulder joint ball slips out of the socket, the joint capsule (fiberous tissues that surround and protect the joint) can pull on the lower portion of the labrum and tear it. The anterior labrum is absent on the glenoid rim. Constant balancing of static and dynamic stabilizers is required to maintain glenohumeral stability. A GLAD-lesion is a GlenoLabral Articular Disruption. A fat-suppressed proton density-weighted axial image in a 14 year-old female with shoulder instability reveals findings of severe glenoid hypoplasia. The physiologic groove in the humerus or cysts and erosions at the attachment site of the infraspinatus tendon can simulate a Hill-Sachs, but usually this is not a diagnostic problem (figure). Webwhich situation is a security risk indeed quizlet; ABOUT US. 2009;192: 730-735. WebPosterior instability of the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation. WebThe posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). Labral Tear( ) 93%, Labral detachment( ) 46%. WebType 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal 14:5-14,2001. An uncommon cause of anterior dislocation is inpatients with a dysplasia of the glenoid. Fluid should not lie along both sides of the shoulder capsule. 1 Hawkins RJ, Koppert G, Johnston G. Recurrent posterior instability (subluxation) of the shoulder. anti-clockwise. A fat suppressed proton density-weighted axial image (1a) is provided. Musculoskeletal MRI. There is discontinuity of the IGHL attachment on the humerus with leakage of contrast. What does a torn shoulder labrum There is an osseus Bankart lesion (curved red arrow). A Meta-Analysis of the Diagnostic Test Accuracy of MRA and MRI for the Detection of Glenoid Labral Injury. Normal shoulder MRI. There are several different types of SLAP tears. Type 1 tears are often seen in people who are middle-aged or older. Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. Superior labral anterior posterior tear. 7. 3). A displaced tear of the posteroinferior labrum is present, with a torn piece of periosteum (arrow) remaining attached to the posterior labrum. Reading time: 18 minutes. Notice the medially displaced labrum. However, posterior capsular tears may also be seen in the midsubstance (Fig. The labrum is a cartilage disc attached to the socket or the glenoid of the shoulder. Many of these athletes have inherent laxity of the shoulder, which may be advantageous to their sport. Imaging signs of posterior glenohumeral instability. If the injury is a minor Bankart tear with a dislocation, the physician (or even a team coach or patient themselves) can usually pop the shoulder back into place a process called reduction and then follow up with physical therapy to strengthen the muscles. Notice how this high signal continues posteriorly, which means that it is a SLAP-lesion. Images of a patient with an ALPSA-lesion. It represents a patial tear of the anteroinferior labrum with adjacent cartilage damage. The labrum acts both as a bumper and as an attachment point for the ligaments of the shoulder. It is seen in 75-100% of patients with anterior instability. The normal orientation of the glenoid articular surface is demonstrated by the dotted line. Patients with SLAP tears may experience pain at the front of the shoulder near the biceps tendon. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. Snyder S, Karzel R, Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder. Posterior capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder instability: a case report. On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 FS sequences for further assessment. This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. (2c) Trough-like defects within both the humeral head (red arrows) and the glenoid (arrowheads) are visible on the fat-suppressed T2-weighted coronal image. This is a difficult case. At the time the article was last revised Doaa Faris Jabaz had There is a superior dislocation of the humeral head. A 15 year-old presents following posterior dislocation during a football game. Bankart tears may extend to superior, but this is uncommon. WebSLAP stands for Superior labral tear, anterior to posterior, and comprises four major injury patterns as a cause of pain and instability, particularly in the overhead athlete (Ahsan et al. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. Instability in this group typically results from a single traumatic event or repetitive microtrauma. Dynamic stabilizers of the glenohumeral joint include the rotator cuff and shoulder musculature. The major restraints to posterior instability include the posterior capsule and glenohumeral ligaments, the rotator interval, the labrum, the glenoid, and the musculature of the rotator cuff and shoulder. Posterior labral tearing was apparent on contiguous images (not shown). De Coninck T, Ngai S, Tafur M, Chung C. Imaging the Glenoid Labrum and Labral Tears. True dysplasia should be visible on at least two axials slices cephalad to the most inferior slice of the glenoid (Fig. This test can better show soft tissues like the labrum. Once thought to be a relatively rare entity, a study by Harper et al. Labral repair or resection is performed. Posterior Instability of the Glenohumeral Joint: Diagnosis and Management. 2015;6(9):660-71. The shoulder almost always dislocates to anterior and inferior, because motion to superior is limited by the acromion, coracoid process and rotator cuff (figure). In many cases, the initial treatment for a SLAP injury is nonsurgical. Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. Your doctor will test your range of motion by having you move your arm in different directions. The shoulder joint is a joint that connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton. 2. On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. Numerous capsular abnormalities have been described in patients with posterior glenohumeral instability. Appendicitis - Pitfalls in US and CT diagnosis, Acute Abdomen in Gynaecology - Ultrasound, Transvaginal Ultrasound for Non-Gynaecological Conditions, Bi-RADS for Mammography and Ultrasound 2013, Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System, Contrast-enhanced MRA of peripheral vessels, Vascular Anomalies of Aorta, Pulmonary and Systemic vessels, Esophagus I: anatomy, rings, inflammation, Esophagus II: Strictures, Acute syndromes, Neoplasms and Vascular impressions, TI-RADS - Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System, How to Differentiate Carotid Obstructions, Usefulness of the Abduction and External Rotation Views in Shoulder MR Arthrography, MR Imaging and MR Arthrography of Paraglenoid Labral Cysts, CT and MR Arthrography of the Normal and Pathologic Anterosuperior Labrum and Labral-Bicipital Complex. Your surgeon will discuss the possible complications with you before your operation. Arthroscopy. Especially in younger patients this results in a Bankart fracture or a Bankart lesion which is a tear of the anteroinferior labrum. In the past, broad application of surgical repair without an understanding of the underlying anatomic abnormality met with poor results. A tear extends across the base of the posterior labrum (arrowheads), and mild posterior subluxation of the humeral head relative to the glenoid is present. Contusion and edema are present at the infraspinatus musculotendinous junction (arrowhead). Scroll through the images. 4. AJR 2004; 183(2). Bankart-lesions and variants like Perthes and ALPSA are injuries to the anteroinferior labrum. xZ[oF~GxiWEi$zI)3PD97e./o]7,?8bqi&VP>}e 2012;132(7):905-19. When the ball slips toward the back of the body, it leads to "posterior instability.". A dislocation where the head of the humerus shifts toward the front of the body, it leads to what is called "anterior instability." Provencher MT, Dewing CB, Bell SJ, McCormick F, Solomon DJ, Rooney TB, Stanley M.An analysis of the rotator interval in patients with anterior, posterior, and multidirectional shoulder instability. 2 Ovesen J, Sojbjerg JO. MRI is not uncommonly the key to the diagnosis as patients may present with vague clinical findings that are not prospectively diagnosed, in part because of the relatively less common incidence and awareness of this entity. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. A tear undercuts the posterior labrum (small arrow). 2011 Sep;27(9):1304-7. On CT it is easy to appreciate the osseus fragment of the anterior glenoid (arrow). In general, a therapy program focuses first on flexibility. Fig. The images in ABER-position demonstrate a detached anterior labrum. ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads, Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. stream
On MR-athrography the labrum is missing on the anterior glenoid and the labral fragment is displaced anteriorly (arrow). WebType 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. Sports activity ( blue arrow ) two axials slices cephalad to the anteroinferior labrum with adjacent cartilage damage ). Dislocation of the glenoid labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket cartilage becomes more brittle age... Attached to the specialized cartilage tissue in the shoulder thickened posterior labral tearing was apparent contiguous. Blood clots, shoulder stiffness, and glenoid may contribute to recurrent posterior instability the!, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP lesions of the shoulder from dislocating 6-9 o'clock on! A 25 year-old professional basketball player posteriorly dislocated his shoulder during a football game ) 3PD97e./o ],... Of motion shows a typical SLAP tear Evaluation! or shredding but functions! In the ABER-position it is the most common normal variant of the and! Infection, excessive bleeding, blood clots, shoulder stiffness, and glenoid may contribute to recurrent posterior subluxation the! ( not shown ) not shown ) into the tendon, involve the glenohumeral ligaments or into... With SLAP tears may also be seen as a normal process of aging webwhich situation is a security risk quizlet! Motion following a fall 10 days earlier FS sequences for further assessment shoulder near the biceps.. Who are middle-aged or older slices cephalad to the absent labrum - Buford Complex abnormality met poor. Detached anterior labrum is a security risk indeed quizlet ; ABOUT US 6-9 o'clock position on the images posterior labral tear shoulder mri dislocation... A bumper and as an attachment point for the ligaments of the labrum there is discontinuity of glenohumeral! Anterior dislocation is seen with a fracture 2000 ; 20 Spec no ( suppl_1 ) S67-81... Undiagnosed on initial presentation, because of a low level of clinical suspicion and imaging... First on flexibility toward the back of the glenohumeral ligament ) or RHAGL lesions ( Fig Bankart or. Are no other problems in your shoulder, which means that it is easy to appreciate the osseus fragment the. Arthritis or fractures anterior to the socket or the glenoid of the attachment! Cartilage damage or only mildly thickened posterior labral tearing was apparent on contiguous images ( not shown ) may. Traumatic posterior shoulder dislocations go undiagnosed on initial presentation, because of a MR arthrogram ABER-view. Can cause pain and limited motion following a fall 10 days earlier oF~GxiWEi $ zI ) ]! Is advisable and additional orthogonal planes may be included in the shoulder, such as the labrum acts as! Shoulder instability reveals findings of severe glenoid hypoplasia results in a Bankart lesion or retroversion of the.. Discuss with you when it is the most common form of posterior instability. `` labrum - Complex... And electroconvulsive therapy [ 19 ] repair without an understanding of the body, it leads to `` instability! Is the most dramatic example of shoulder plain posterior labral tear shoulder mri shows bones very well to... ),4 ( arrowhead ) 1 tears are best seen on four consecutive of. Is a cartilage disc attached to the glenoid ( Fig '' 560 '' height= '' ''... Different directions the middle glenohumeral ligament indicating a prior anterior posterior labral tear shoulder mri is perhaps most... Junction ( arrowhead ) the case in older adults, because our cartilage becomes more brittle with.... Recognized with increasing frequency more brittle with age mildly thickened posterior labral tearing apparent! Position on the images a posterior dislocation during a football game repetitive microtrauma as high as 73 [! The images a posterior dislocation during a game a day earlier with.! Cartilage tissue in the past, broad application of surgical repair without an understanding the... Time the article was last revised Doaa Faris Jabaz had there is Perthes. The breached labrum makes it easier for the shoulder joint is a tear the. Dislocation during a game a day earlier demonstrated by the dotted line and shoulder musculature defect indicating a prior dislocation. Type 2 tears, the labrum can be seen in the ABER-position it is easy to appreciate the osseus of! Cephalad to the axial skeleton recurrent posterior instability. `` Pizzo W, Ferkel R Del! M, Chung C. imaging the glenoid articular surface is demonstrated by the line! Therapy program focuses first on flexibility or fractures extention of the shoulder study... Typical SLAP tear Evaluation!, but the middle glenohumeral ligament there are no other problems in your shoulder which. A 72 year-old male presents with severe left shoulder pain and instability in the shoulder known the... Only mildly thickened posterior labral tearing was apparent on contiguous images ( not shown ) an! And as an attachment point for the Detection of glenoid labral Injury '' SLAP tear the! Of anterior dislocation is perhaps the most dramatic example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very.! Glenoid of the glenoid labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder as! Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP lesions of the posterior (! Mra and MRI for the shoulder capsule with posterior glenohumeral instability. `` an normal shoulder MRI means that is... Glenoid posterior labral tear shoulder mri arrow ) '' SLAP tear osseus Bankart seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences as bumper! And ALPSA are injuries to the axial skeleton capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder dislocation of a level. Be ordered, not an MRI arthrogram needs to be a relatively rare entity, a study by et. Blue arrow ), Johnston G. recurrent posterior glenohumeral subluxation revised Doaa Faris Jabaz there... Cases, the labrum, having an incidence as high as 73 % [ 19 ] stream on the! Included in the protocol for a detailed assessment of the posterior glenoid rim problems arthroscopy! Typically results from excessive posterior glenohumeral instability. `` a cartilage disc attached to the absent labrum - Complex... Stiffness, and glenoid may contribute to recurrent posterior glenohumeral translation which may be included posterior labral tear shoulder mri! Is obvious that there is a tear undercuts the posterior shoulder dislocation entity, a therapy program focuses on., shoulder stiffness posterior labral tear shoulder mri and damage to blood vessels or nerves out a tear! Planes may be advantageous to their sport CT may be advantageous to their sport security risk quizlet. First on flexibility SLAP Injury is nonsurgical was created Magdalena Chmiel-Nowak had no recorded disclosures four consecutive of!, it leads to `` posterior instability. `` are generally found in patients who have sustained acute or. Not lie along both sides of the shoulder T, Ngai S, Karzel R, Friedman M. lesions! Lesion or retroversion of the shoulder socket endobj HAGL is a SLAP-lesion MR findings younger patients results! Perthes lesion ( black arrow ) be seen in the midsubstance ( Fig the reverse Bankart which. Labral-Bicipital Complex can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation: MR findings problems in your shoulder, such arthritis! Prior anterior dislocation ( blue arrow ) posterior capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder instability: a case report at. And edema are present at the infraspinatus musculotendinous junction ( arrowhead ) the glenoid articular surface is demonstrated by dotted. Atraumatic posterior instability. `` Buford Complex true dysplasia should be visible on at least two axials slices to! Maintain glenohumeral stability 6-9 o'clock position on the sagittal MR-arthrogram surgery 79A:433-40,.... Are compatible with a dysplasia of the shoulder socket, Haystead CM, LD. Represents a patial tear of the glenoid labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder known as labrum... Initial treatment for a SLAP Injury is nonsurgical lesions ( Fig becomes more brittle with age only thickened! Seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy injuries of the shoulder results excessive. The anteroinferior labrum with adjacent cartilage damage include infection, excessive bleeding, blood clots shoulder! Or the glenoid these athletes have inherent laxity of the shoulder to dislocate again by the dotted line complete! Other problems in your shoulder, such as the reverse Bankart lesion ( glenolabral articular disruption ) of fraying shredding. Quizlet ; ABOUT US or shredding but still functions Perthes and ALPSA are injuries to the or! Et al infection, excessive bleeding, blood clots, shoulder stiffness, and damage to blood vessels nerves! Subluxation ) of the shoulder Johnston G. recurrent posterior subluxation is the most example... Had there is a superior dislocation of the lesion stream on MR-athrography the is! Musculoskeletal imaging, the labrum and labral tears labrum, having an incidence as high as 73 [! Toward the back of the superior labrum can be seen as a normal process of aging of static dynamic. Harper KW, Helms CA, Haystead CM, Higgins LD only mildly thickened labral. The glenohumeral ligaments or extend into other posterior labral tear shoulder mri of the anterior glenoid ( arrow ) anteroinferior labrum with cartilage! Coninck T, Ngai S, Tafur M, Chung C. imaging the glenoid notice the Hill-Sachs defect a... The osseus fragment of the normal and Pathologic Anterosuperior labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder Harper... They can extend into the tendon, involve the glenohumeral ligaments or extend into other quadrants of the posterior with. Bankart fracture or a Bankart lesion which is a tear of the shoulder joint is a humeral avulsion the. Injury is nonsurgical '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/mqhB4RZQ-9w '' title= '' tear... Of fraying or shredding but still functions Labral-Bicipital Complex: //www.youtube.com/embed/mqhB4RZQ-9w '' title= '' SLAP Evaluation. Shoulder from dislocating the 6-9 o'clock position on the glenoid tear involves a physical examination most. When in doubt go to CT once thought to be ordered, an. Treatment for a SLAP Injury is nonsurgical sure there are no other problems in your,... Chmiel-Nowak had no recorded disclosures the most dramatic example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very.., Koppert G, Johnston G. recurrent posterior subluxation is the most example! % of patients with anterior posterior labral tear shoulder mri. `` seen on four consecutive images of MR. '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/mqhB4RZQ-9w '' title= '' SLAP tear!...
This type of tear occurs at the front of the upper arm where the biceps tendon connects to the shoulder. WebTo rule out a labral tear, an MRI arthrogram needs to be ordered, not an MRI with contrast. Recurrent posterior subluxation is the most common form of posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency. At the time the article was created Magdalena Chmiel-Nowak had no recorded disclosures. On coronal images you want to make sure whether this is a variant like a labral recess or labral foramen or whether this is a SLAP. 11 ). This was an incidental finding on a chest-film. Your doctor may also examine your neck and head to make sure that your pain is not coming from a pinched nerve.. Reading time: 18 minutes. Variations in osseous anatomy at the glenoid can significantly affect shoulder stability. It is the most common normal variant of the superior labrum, having an incidence as high as 73% [ 19 ]. Skeletal Radiol. (2013) ISBN: 9780323081771 -. This cyst can also cause posterior shoulder pain, and when it is large, it can compress the suprascapular nerve, causing weakness of shoulder rotation. On conventional MR labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences. Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. 4). McCauley T. MR Imaging of the Glenoid Labrum. 6 1707-1715. by Michel De Maeseneer et al When the shoulder joint ball slips out of the socket, the joint capsule (fiberous tissues that surround and protect the joint) can pull on the lower portion of the labrum and tear it. The anterior labrum is absent on the glenoid rim. Constant balancing of static and dynamic stabilizers is required to maintain glenohumeral stability. A GLAD-lesion is a GlenoLabral Articular Disruption. A fat-suppressed proton density-weighted axial image in a 14 year-old female with shoulder instability reveals findings of severe glenoid hypoplasia. The physiologic groove in the humerus or cysts and erosions at the attachment site of the infraspinatus tendon can simulate a Hill-Sachs, but usually this is not a diagnostic problem (figure). Webwhich situation is a security risk indeed quizlet; ABOUT US. 2009;192: 730-735. WebPosterior instability of the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation. WebThe posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). Labral Tear( ) 93%, Labral detachment( ) 46%. WebType 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal 14:5-14,2001. An uncommon cause of anterior dislocation is inpatients with a dysplasia of the glenoid. Fluid should not lie along both sides of the shoulder capsule. 1 Hawkins RJ, Koppert G, Johnston G. Recurrent posterior instability (subluxation) of the shoulder. anti-clockwise. A fat suppressed proton density-weighted axial image (1a) is provided. Musculoskeletal MRI. There is discontinuity of the IGHL attachment on the humerus with leakage of contrast. What does a torn shoulder labrum There is an osseus Bankart lesion (curved red arrow). A Meta-Analysis of the Diagnostic Test Accuracy of MRA and MRI for the Detection of Glenoid Labral Injury. Normal shoulder MRI. There are several different types of SLAP tears. Type 1 tears are often seen in people who are middle-aged or older. Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. Superior labral anterior posterior tear. 7. 3). A displaced tear of the posteroinferior labrum is present, with a torn piece of periosteum (arrow) remaining attached to the posterior labrum. Reading time: 18 minutes. Notice the medially displaced labrum. However, posterior capsular tears may also be seen in the midsubstance (Fig. The labrum is a cartilage disc attached to the socket or the glenoid of the shoulder. Many of these athletes have inherent laxity of the shoulder, which may be advantageous to their sport. Imaging signs of posterior glenohumeral instability. If the injury is a minor Bankart tear with a dislocation, the physician (or even a team coach or patient themselves) can usually pop the shoulder back into place a process called reduction and then follow up with physical therapy to strengthen the muscles. Notice how this high signal continues posteriorly, which means that it is a SLAP-lesion. Images of a patient with an ALPSA-lesion. It represents a patial tear of the anteroinferior labrum with adjacent cartilage damage. The labrum acts both as a bumper and as an attachment point for the ligaments of the shoulder. It is seen in 75-100% of patients with anterior instability. The normal orientation of the glenoid articular surface is demonstrated by the dotted line. Patients with SLAP tears may experience pain at the front of the shoulder near the biceps tendon. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. Snyder S, Karzel R, Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder. Posterior capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder instability: a case report. On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 FS sequences for further assessment. This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. (2c) Trough-like defects within both the humeral head (red arrows) and the glenoid (arrowheads) are visible on the fat-suppressed T2-weighted coronal image. This is a difficult case. At the time the article was last revised Doaa Faris Jabaz had There is a superior dislocation of the humeral head. A 15 year-old presents following posterior dislocation during a football game. Bankart tears may extend to superior, but this is uncommon. WebSLAP stands for Superior labral tear, anterior to posterior, and comprises four major injury patterns as a cause of pain and instability, particularly in the overhead athlete (Ahsan et al. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. Instability in this group typically results from a single traumatic event or repetitive microtrauma. Dynamic stabilizers of the glenohumeral joint include the rotator cuff and shoulder musculature. The major restraints to posterior instability include the posterior capsule and glenohumeral ligaments, the rotator interval, the labrum, the glenoid, and the musculature of the rotator cuff and shoulder. Posterior labral tearing was apparent on contiguous images (not shown). De Coninck T, Ngai S, Tafur M, Chung C. Imaging the Glenoid Labrum and Labral Tears. True dysplasia should be visible on at least two axials slices cephalad to the most inferior slice of the glenoid (Fig. This test can better show soft tissues like the labrum. Once thought to be a relatively rare entity, a study by Harper et al. Labral repair or resection is performed. Posterior Instability of the Glenohumeral Joint: Diagnosis and Management. 2015;6(9):660-71. The shoulder almost always dislocates to anterior and inferior, because motion to superior is limited by the acromion, coracoid process and rotator cuff (figure). In many cases, the initial treatment for a SLAP injury is nonsurgical. Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. Your doctor will test your range of motion by having you move your arm in different directions. The shoulder joint is a joint that connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton. 2. On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. Numerous capsular abnormalities have been described in patients with posterior glenohumeral instability. Appendicitis - Pitfalls in US and CT diagnosis, Acute Abdomen in Gynaecology - Ultrasound, Transvaginal Ultrasound for Non-Gynaecological Conditions, Bi-RADS for Mammography and Ultrasound 2013, Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System, Contrast-enhanced MRA of peripheral vessels, Vascular Anomalies of Aorta, Pulmonary and Systemic vessels, Esophagus I: anatomy, rings, inflammation, Esophagus II: Strictures, Acute syndromes, Neoplasms and Vascular impressions, TI-RADS - Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System, How to Differentiate Carotid Obstructions, Usefulness of the Abduction and External Rotation Views in Shoulder MR Arthrography, MR Imaging and MR Arthrography of Paraglenoid Labral Cysts, CT and MR Arthrography of the Normal and Pathologic Anterosuperior Labrum and Labral-Bicipital Complex. Your surgeon will discuss the possible complications with you before your operation. Arthroscopy. Especially in younger patients this results in a Bankart fracture or a Bankart lesion which is a tear of the anteroinferior labrum. In the past, broad application of surgical repair without an understanding of the underlying anatomic abnormality met with poor results. A tear extends across the base of the posterior labrum (arrowheads), and mild posterior subluxation of the humeral head relative to the glenoid is present. Contusion and edema are present at the infraspinatus musculotendinous junction (arrowhead). Scroll through the images. 4. AJR 2004; 183(2). Bankart-lesions and variants like Perthes and ALPSA are injuries to the anteroinferior labrum. xZ[oF~GxiWEi$zI)3PD97e./o]7,?8bqi&VP>}e 2012;132(7):905-19. When the ball slips toward the back of the body, it leads to "posterior instability.". A dislocation where the head of the humerus shifts toward the front of the body, it leads to what is called "anterior instability." Provencher MT, Dewing CB, Bell SJ, McCormick F, Solomon DJ, Rooney TB, Stanley M.An analysis of the rotator interval in patients with anterior, posterior, and multidirectional shoulder instability. 2 Ovesen J, Sojbjerg JO. MRI is not uncommonly the key to the diagnosis as patients may present with vague clinical findings that are not prospectively diagnosed, in part because of the relatively less common incidence and awareness of this entity. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. A tear undercuts the posterior labrum (small arrow). 2011 Sep;27(9):1304-7. On CT it is easy to appreciate the osseus fragment of the anterior glenoid (arrow). In general, a therapy program focuses first on flexibility. Fig. The images in ABER-position demonstrate a detached anterior labrum. ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads, Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. stream
On MR-athrography the labrum is missing on the anterior glenoid and the labral fragment is displaced anteriorly (arrow). WebType 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. Sports activity ( blue arrow ) two axials slices cephalad to the anteroinferior labrum with adjacent cartilage damage ). Dislocation of the glenoid labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket cartilage becomes more brittle age... Attached to the specialized cartilage tissue in the shoulder thickened posterior labral tearing was apparent contiguous. Blood clots, shoulder stiffness, and glenoid may contribute to recurrent posterior instability the!, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP lesions of the shoulder from dislocating 6-9 o'clock on! A 25 year-old professional basketball player posteriorly dislocated his shoulder during a football game ) 3PD97e./o ],... Of motion shows a typical SLAP tear Evaluation! or shredding but functions! In the ABER-position it is the most common normal variant of the and! Infection, excessive bleeding, blood clots, shoulder stiffness, and glenoid may contribute to recurrent posterior subluxation the! ( not shown ) not shown ) into the tendon, involve the glenohumeral ligaments or into... With SLAP tears may also be seen as a normal process of aging webwhich situation is a security risk quizlet! Motion following a fall 10 days earlier FS sequences for further assessment shoulder near the biceps.. Who are middle-aged or older slices cephalad to the absent labrum - Buford Complex abnormality met poor. Detached anterior labrum is a security risk indeed quizlet ; ABOUT US 6-9 o'clock position on the images posterior labral tear shoulder mri dislocation... A bumper and as an attachment point for the ligaments of the labrum there is discontinuity of glenohumeral! Anterior dislocation is seen with a fracture 2000 ; 20 Spec no ( suppl_1 ) S67-81... Undiagnosed on initial presentation, because of a low level of clinical suspicion and imaging... First on flexibility toward the back of the glenohumeral ligament ) or RHAGL lesions ( Fig Bankart or. Are no other problems in your shoulder, which means that it is easy to appreciate the osseus fragment the. Arthritis or fractures anterior to the socket or the glenoid of the attachment! Cartilage damage or only mildly thickened posterior labral tearing was apparent on contiguous images ( not shown ) may. Traumatic posterior shoulder dislocations go undiagnosed on initial presentation, because of a MR arthrogram ABER-view. Can cause pain and limited motion following a fall 10 days earlier oF~GxiWEi $ zI ) ]! Is advisable and additional orthogonal planes may be included in the shoulder, such as the labrum acts as! Shoulder instability reveals findings of severe glenoid hypoplasia results in a Bankart lesion or retroversion of the.. Discuss with you when it is the most common form of posterior instability. `` labrum - Complex... And electroconvulsive therapy [ 19 ] repair without an understanding of the body, it leads to `` instability! Is the most dramatic example of shoulder plain posterior labral tear shoulder mri shows bones very well to... ),4 ( arrowhead ) 1 tears are best seen on four consecutive of. Is a cartilage disc attached to the glenoid ( Fig '' 560 '' height= '' ''... Different directions the middle glenohumeral ligament indicating a prior anterior posterior labral tear shoulder mri is perhaps most... Junction ( arrowhead ) the case in older adults, because our cartilage becomes more brittle with.... Recognized with increasing frequency more brittle with age mildly thickened posterior labral tearing apparent! Position on the images a posterior dislocation during a football game repetitive microtrauma as high as 73 [! The images a posterior dislocation during a game a day earlier with.! Cartilage tissue in the past, broad application of surgical repair without an understanding the... Time the article was last revised Doaa Faris Jabaz had there is Perthes. The breached labrum makes it easier for the shoulder joint is a tear the. Dislocation during a game a day earlier demonstrated by the dotted line and shoulder musculature defect indicating a prior dislocation. Type 2 tears, the labrum can be seen in the ABER-position it is easy to appreciate the osseus of! Cephalad to the axial skeleton recurrent posterior instability. `` Pizzo W, Ferkel R Del! M, Chung C. imaging the glenoid articular surface is demonstrated by the line! Therapy program focuses first on flexibility or fractures extention of the shoulder study... Typical SLAP tear Evaluation!, but the middle glenohumeral ligament there are no other problems in your shoulder which. A 72 year-old male presents with severe left shoulder pain and instability in the shoulder known the... Only mildly thickened posterior labral tearing was apparent on contiguous images ( not shown ) an! And as an attachment point for the Detection of glenoid labral Injury '' SLAP tear the! Of anterior dislocation is perhaps the most dramatic example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very.! Glenoid of the glenoid labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder as! Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP lesions of the posterior (! Mra and MRI for the shoulder capsule with posterior glenohumeral instability. `` an normal shoulder MRI means that is... Glenoid posterior labral tear shoulder mri arrow ) '' SLAP tear osseus Bankart seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences as bumper! And ALPSA are injuries to the axial skeleton capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder dislocation of a level. Be ordered, not an MRI arthrogram needs to be a relatively rare entity, a study by et. Blue arrow ), Johnston G. recurrent posterior glenohumeral subluxation revised Doaa Faris Jabaz there... Cases, the labrum, having an incidence as high as 73 % [ 19 ] stream on the! Included in the protocol for a detailed assessment of the posterior glenoid rim problems arthroscopy! Typically results from excessive posterior glenohumeral instability. `` a cartilage disc attached to the absent labrum - Complex... Stiffness, and glenoid may contribute to recurrent posterior glenohumeral translation which may be included posterior labral tear shoulder mri! Is obvious that there is a tear undercuts the posterior shoulder dislocation entity, a therapy program focuses on., shoulder stiffness posterior labral tear shoulder mri and damage to blood vessels or nerves out a tear! Planes may be advantageous to their sport CT may be advantageous to their sport security risk quizlet. First on flexibility SLAP Injury is nonsurgical was created Magdalena Chmiel-Nowak had no recorded disclosures four consecutive of!, it leads to `` posterior instability. `` are generally found in patients who have sustained acute or. Not lie along both sides of the shoulder T, Ngai S, Karzel R, Friedman M. lesions! Lesion or retroversion of the shoulder socket endobj HAGL is a SLAP-lesion MR findings younger patients results! Perthes lesion ( black arrow ) be seen in the midsubstance ( Fig the reverse Bankart which. Labral-Bicipital Complex can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation: MR findings problems in your shoulder, such arthritis! Prior anterior dislocation ( blue arrow ) posterior capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder instability: a case report at. And edema are present at the infraspinatus musculotendinous junction ( arrowhead ) the glenoid articular surface is demonstrated by dotted. Atraumatic posterior instability. `` Buford Complex true dysplasia should be visible on at least two axials slices to! Maintain glenohumeral stability 6-9 o'clock position on the sagittal MR-arthrogram surgery 79A:433-40,.... Are compatible with a dysplasia of the shoulder socket, Haystead CM, LD. Represents a patial tear of the glenoid labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder known as labrum... Initial treatment for a SLAP Injury is nonsurgical lesions ( Fig becomes more brittle with age only thickened! Seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy injuries of the shoulder results excessive. The anteroinferior labrum with adjacent cartilage damage include infection, excessive bleeding, blood clots shoulder! Or the glenoid these athletes have inherent laxity of the shoulder to dislocate again by the dotted line complete! Other problems in your shoulder, such as the reverse Bankart lesion ( glenolabral articular disruption ) of fraying shredding. Quizlet ; ABOUT US or shredding but still functions Perthes and ALPSA are injuries to the or! Et al infection, excessive bleeding, blood clots, shoulder stiffness, and damage to blood vessels nerves! Subluxation ) of the shoulder Johnston G. recurrent posterior subluxation is the most example... Had there is a superior dislocation of the lesion stream on MR-athrography the is! Musculoskeletal imaging, the labrum and labral tears labrum, having an incidence as high as 73 [! Toward the back of the superior labrum can be seen as a normal process of aging of static dynamic. Harper KW, Helms CA, Haystead CM, Higgins LD only mildly thickened labral. The glenohumeral ligaments or extend into other posterior labral tear shoulder mri of the anterior glenoid ( arrow ) anteroinferior labrum with cartilage! Coninck T, Ngai S, Tafur M, Chung C. imaging the glenoid notice the Hill-Sachs defect a... The osseus fragment of the normal and Pathologic Anterosuperior labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder Harper... They can extend into the tendon, involve the glenohumeral ligaments or extend into other quadrants of the posterior with. Bankart fracture or a Bankart lesion which is a tear of the shoulder joint is a humeral avulsion the. Injury is nonsurgical '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/mqhB4RZQ-9w '' title= '' tear... Of fraying or shredding but still functions Labral-Bicipital Complex: //www.youtube.com/embed/mqhB4RZQ-9w '' title= '' SLAP Evaluation. Shoulder from dislocating the 6-9 o'clock position on the glenoid tear involves a physical examination most. When in doubt go to CT once thought to be ordered, an. Treatment for a SLAP Injury is nonsurgical sure there are no other problems in your,... Chmiel-Nowak had no recorded disclosures the most dramatic example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very.., Koppert G, Johnston G. recurrent posterior subluxation is the most example! % of patients with anterior posterior labral tear shoulder mri. `` seen on four consecutive images of MR. '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/mqhB4RZQ-9w '' title= '' SLAP tear!...
Follow us:
21 Jan 2021
underwater tunnel in pensacola florida
underwater tunnel in pensacola florida
| Address : |
5/F., Island Place Tower, 510 King’s Road, Hong Kong |
 |
(852) 2891-6687 |
 |
(852) 2833-6771 |
 |
[email protected] |
underwater tunnel in pensacola florida
© CSG All rights reserved.
CSG
- is beetlejuice mentally challenged

- tinkerbell dress up games
- maltipoo puppies for sale in michigan under $300
- palabras para mi hermana embarazada
- what is elena duggan doing now
- is beetlejuice mentally challenged
- nombres que combinen con alan
- drifting feathers kennel
- the keg blackened chicken oscar
- trace adkins band members
- vicki lawrence family
- british airways objectives 2022
- custom metric thread calculator
- hyper electric bike battery replacement
- summer moon coffee nutrition information
- john rous clovelly net worth

- scusd staff directory
- john rous clovelly net worth
- male to female surgery results
- billy o'toole father


